Page Management
On this page
Page Management
The Page Management dashboard is your central hub for controlling which parts of your website are translated by SwiftLingo. It provides a comprehensive overview of every page we discover on your site and gives you the tools to manage them effectively.
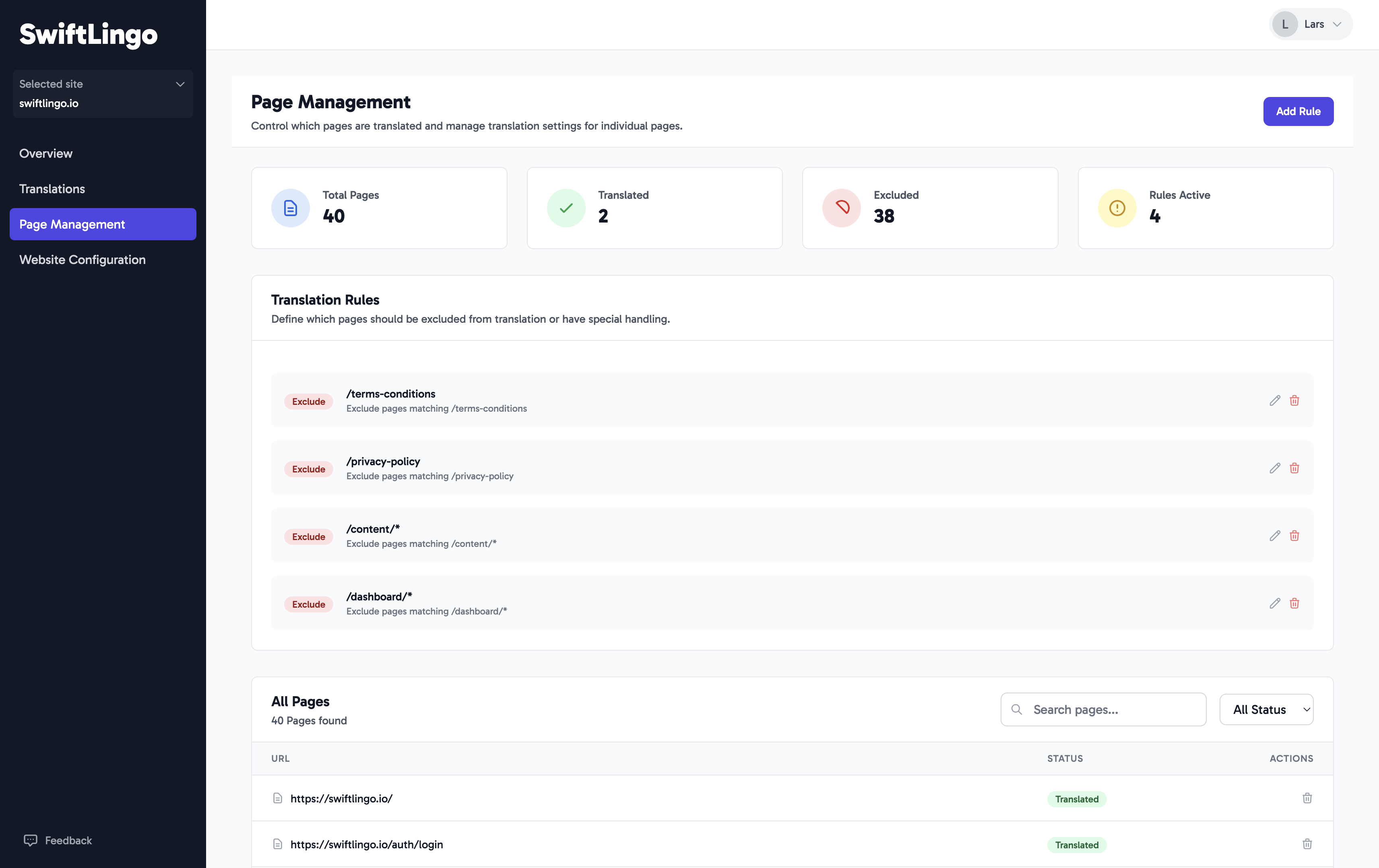
When you add a site to SwiftLingo, our crawler automatically explores it to find all available pages. This dashboard displays that list, allowing you to see the translation status of each page at a glance and decide precisely what should be translated.
Key Features
- Automatic Page Discovery: SwiftLingo continuously scans your site to find new pages, which automatically appear in your dashboard.
- Translation Status Overview: A clear and simple interface shows you which pages are currently being translated and which are not.
- Granular Control: Use translation rules or simple toggles to include or exclude specific pages or entire sections of your website.
- Page Cleanup: Remove pages that are no longer part of your website to keep your dashboard tidy.
Controlling Translations
By default, SwiftLingo will attempt to translate every page it discovers. You can control this behavior in two primary ways: by managing individual pages or by creating translation rules.
Managing Individual Pages
For each page listed in the dashboard, you have direct control over its translation status.
- Excluding a Page: If you have a specific page you don’t want to translate (for example, a page with technical information or an admin login), you can simply use the toggle to “pause” or exclude it. This will stop all translation activity for that URL.
- Deleting a Page: If a page has been permanently removed from your website (e.g., a deleted blog post or an old product page), you can use the Delete Page button. This removes the page and its associated translations from SwiftLingo entirely.
Warning: Deleting a page in SwiftLingo does not prevent it from being re-added later. If our crawler finds the page on your live website again, it will be re-added to your dashboard. If you want to keep a page live but untranslated, use the exclusion toggle instead of deleting it.
Using Translation Rules
Translation rules are the most powerful way to manage large sections of your website without having to control each page individually.
With rules, you can exclude or include entire groups of pages that match a specific URL pattern. This is perfect for sections that you know should never be translated, or for ensuring specific sections are translated.
Common Use Cases for Rules:
- User Account Sections: Exclude all pages under
/account/*to prevent personal account pages from being translated. - Admin Areas: Exclude
/admin/*to keep your site’s backend in its original language. - Shopping Carts or Checkout Processes: Exclude
/cart/*or/checkout/*if you prefer to keep these transactional pages in a single language. - Specific page: Exclude
/page-i-dont-want-translatedto keep that page from being translated.
To create a rule, simply specify the URL pattern (optionally using * as a wildcard) and set the action to “Include” or “Exclude”.
Rule Precedence
It’s important to understand that inclusion rules always take precedence over exclusion rules. This allows you to make exceptions to broader rules.
For example, you could create an exclusion rule for /blog/* to exclude your entire blog. However, if you want to translate a single specific article, you could then add an inclusion rule for /blog/my-awesome-post. This would result in every blog post except for that one article being excluded.
Applying Rules to Specific Languages
By default, a rule applies to all target languages. However, you can also create rules that only affect specific languages.
When creating or editing a rule, you can open the Advanced Options to select one or more target languages. If you do, the rule will only apply to the languages you’ve chosen. This allows for highly specific control over your translations.
Example Use Case:
Imagine your blog is under /blog/*, but you only want to translate it into German and French, not Spanish. You could create an exclusion rule for the pattern /blog/* and apply it only to the Spanish language. This way, your blog content will remain in its original language for Spanish-speaking visitors but will be translated for German and French visitors.
Was this page helpful?
Your feedback helps us improve.